Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, has been at the forefront of discussions about hair health and hair loss. This water-soluble vitamin plays a vital role in various bodily functions, particularly in maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. Recent research has sparked review of the link between biotin and hair loss, offering new insights into its efficacy and the consequences of biotin deficiency.
The Role of Biotin in Hair Health
Biotin is essential for the production of keratin, a fundamental protein that constitutes hair, skin, and nails. This vitamin supports the infrastructure of keratin, promoting stronger and healthier hair. The body’s inability to synthesize biotin requires us to consume it through diet or supplements, emphasizing its importance in daily nutrition.
New Research on Biotin and Hair Loss
Recent studies shed light on biotin’s complex role in hair health. Biotin, a vitamin B7, is known to help those with a deficiency by improving hair growth and reducing shedding. However, high-dose biotin supplementation raises several concerns and may rear other health issues.
High levels of biotin can interfere with lab tests, affecting results for thyroid function and other key markers, which might lead to misdiagnoses. Excessive biotin intake can also cause skin issues like rashes and cystic acne, possibly due to disrupting the balance of other B vitamins. Digestive problems, including nausea and diarrhea, are another potential downside, and while biotin is water-soluble, very high doses could still lead to toxicity, manifesting as excessive thirst and frequent urination.
For those without a biotin deficiency, the benefits of supplementation are less clear. Some studies suggest improvements in hair thickness and shine, but results vary, and not everyone experiences noticeable benefits.
In summary, while biotin can be beneficial for those with a deficiency, its effectiveness for the general population is debated. The potential risks of high-dose supplementation highlight the importance of consulting a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Biotin Deficiency and Hair Loss
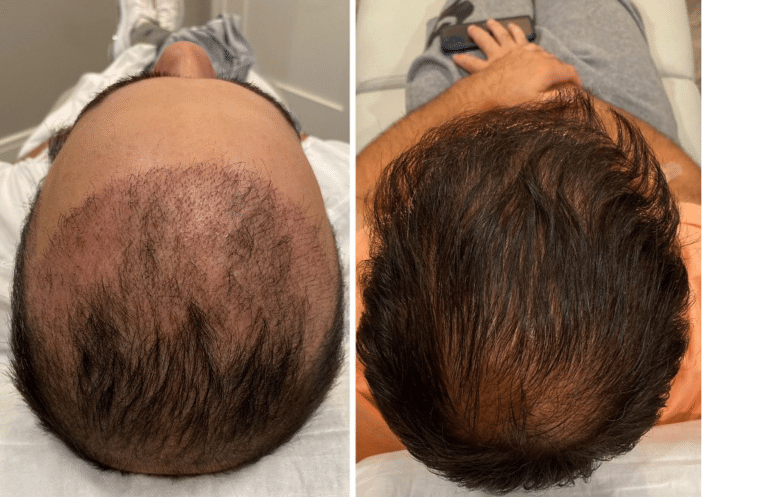
A deficiency in biotin can lead to various health issues, including noticeable hair loss. Symptoms of biotin deficiency may include thinning hair, brittle nails, and skin rashes. In severe cases, it can also result in neurological symptoms such as depression, lethargy, and hallucinations. The deficiency may stem from inadequate dietary intake, chronic consumption of raw egg whites (which contain avidin, a protein that binds biotin and prevents its absorption), or genetic disorders affecting biotin metabolism.
Addressing Biotin Deficiency
Ensuring an adequate intake of biotin is vital for maintaining hair health. Foods rich in biotin include eggs (cooked), nuts, seeds, fish, meat, and certain vegetables like sweet potatoes and spinach. For individuals unable to meet their biotin needs through diet alone, supplements can serve as an effective alternative. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any supplementation, as they can provide personalized recommendations based on individual health needs and conditions.
Misconceptions and Considerations
Despite the positive findings, several misconceptions surround the use of biotin for hair loss. One common misconception is that biotin can completely reverse genetic hair loss conditions such as androgenetic alopecia. While biotin may enhance overall hair health, it is not a cure for genetic hair loss and should be seen as part of a comprehensive hair care regimen.
Another consideration is the potential for over-supplementation. Excessive intake of biotin, although generally considered safe, may interfere with certain laboratory tests, leading to inaccurate results. Therefore, it is crucial to adhere to recommended dosages and consult healthcare professionals when integrating biotin supplements into one’s routine.
Personal Experiences and Testimonials
Many individuals have shared personal stories and testimonials about the positive impact of biotin on their hair health. These accounts often highlight improvements in hair strength, thickness, and growth rate after consistent biotin supplementation. However, individual responses can vary, underscoring the importance of personalized approaches to hair care.
Ultimate Guide to Biotin for Hair Loss in a Glance:
Biotin remains a significant player in the quest for healthy hair. Emerging research supports its role in combating hair loss, particularly for those with a deficiency. While not a standalone solution for all types of hair loss, biotin can contribute to an effective hair care strategy when combined with other treatments and a balanced diet. Embracing a holistic approach to hair health, including proper nutrition and consultation with healthcare providers, can lead to optimal outcomes for those seeking to enhance their hair’s vitality and appearance.
FAQ
1.What is biotin, and how does it affect hair growth?
Biotin, a B vitamin, plays a crucial role in the production of keratin, which is essential for healthy hair growth. It supports the infrastructure of hair, leading to stronger and healthier strands.
2. Can biotin really prevent hair loss?
Biotin can help reduce hair loss in individuals with a biotin deficiency. It may also improve hair thickness and strength in those without a deficiency, but it is not a cure for genetic hair loss conditions.
3. What are the symptoms of biotin deficiency related to hair?
Symptoms of biotin deficiency include thinning hair, hair loss, brittle nails, and skin rashes. In severe cases, neurological symptoms such as depression and lethargy may occur.
4. How much biotin should be taken to improve hair health?
The recommended daily intake of biotin varies, but many supplements contain doses ranging from 2,500 to 10,000 micrograms. Consulting a healthcare provider is advisable to determine the appropriate dosage for individual needs.
5. Are there any side effects of taking biotin supplements?
Biotin is generally considered safe, but excessive intake can interfere with certain lab tests, leading to inaccurate results. Adhering to recommended dosages and consulting with healthcare providers can reduce potential risks.
6. How long does it take to see results from biotin supplementation for hair loss?
Results from biotin supplementation can vary, but many individuals report noticeable improvements in hair health within 3 to 6 months of consistent use.
7. Can biotin be obtained through diet alone?
Yes, biotin can be obtained from dietary sources such as eggs (cooked), nuts, seeds, fish, meat, and certain vegetables like sweet potatoes and spinach. A balanced diet can help maintain adequate biotin levels.
8. Is biotin effective for all types of hair loss?
Biotin is most effective for hair loss due to a deficiency. It can improve hair health in general, but it is not a cure for genetic conditions like androgenetic alopecia.
9. Can biotin supplements be taken with other hair loss treatments?
Biotin supplements can often be combined with other hair loss treatments, such as minoxidil or finasteride. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures that the combination is safe and effective.
10. What are some common misconceptions about biotin and hair loss?
Common misconceptions include the belief that biotin can completely reverse genetic hair loss and that higher doses always lead to better results. Understanding biotin’s role and realistic outcomes is crucial for effective hair care.
Resources
1. National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements
2. American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)
3. Mayo Clinic
4. Healthline
5. PubMed
For more information, read our blogs at https://DrDoris.com/Blogs